Member-only story

Modern cloud native computing heavily relies on the use of containers and the adoption of Kubernetes. Despite being a relatively new technology, it is deployed by many global enterprises to manage business-critical applications in their production environments. The popularity of Kubernetes is driven by a growing range of features, such as enhanced security, better management of microservices, improved observability, and more efficient scaling and resource use.
In this article, we take a look at the essence of technology, its architecture, and its real-world applications.
What is Kubernetes?
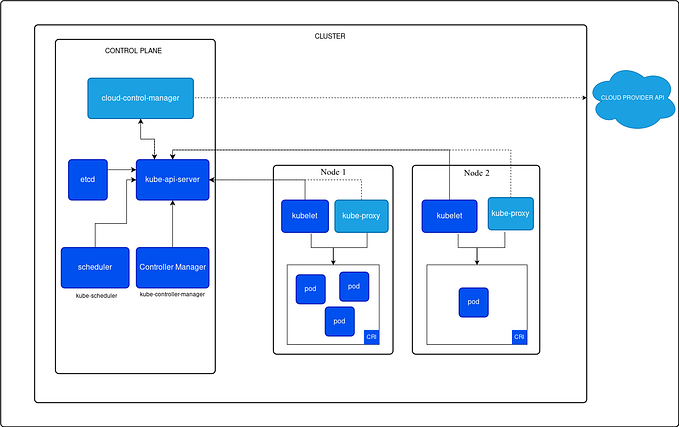
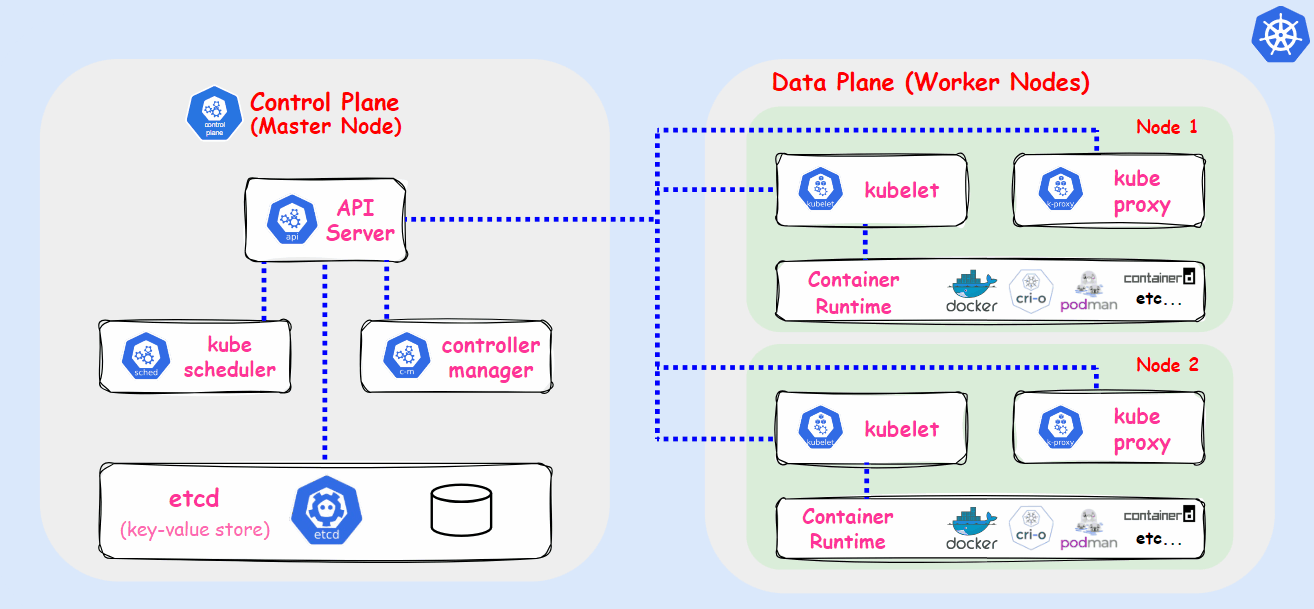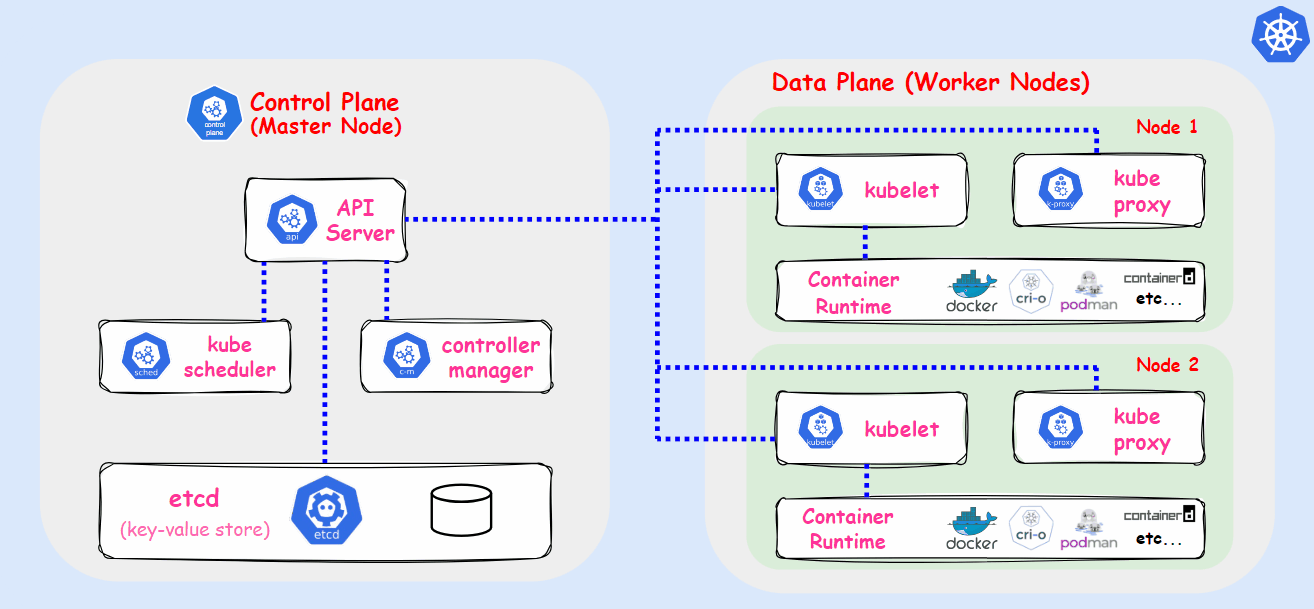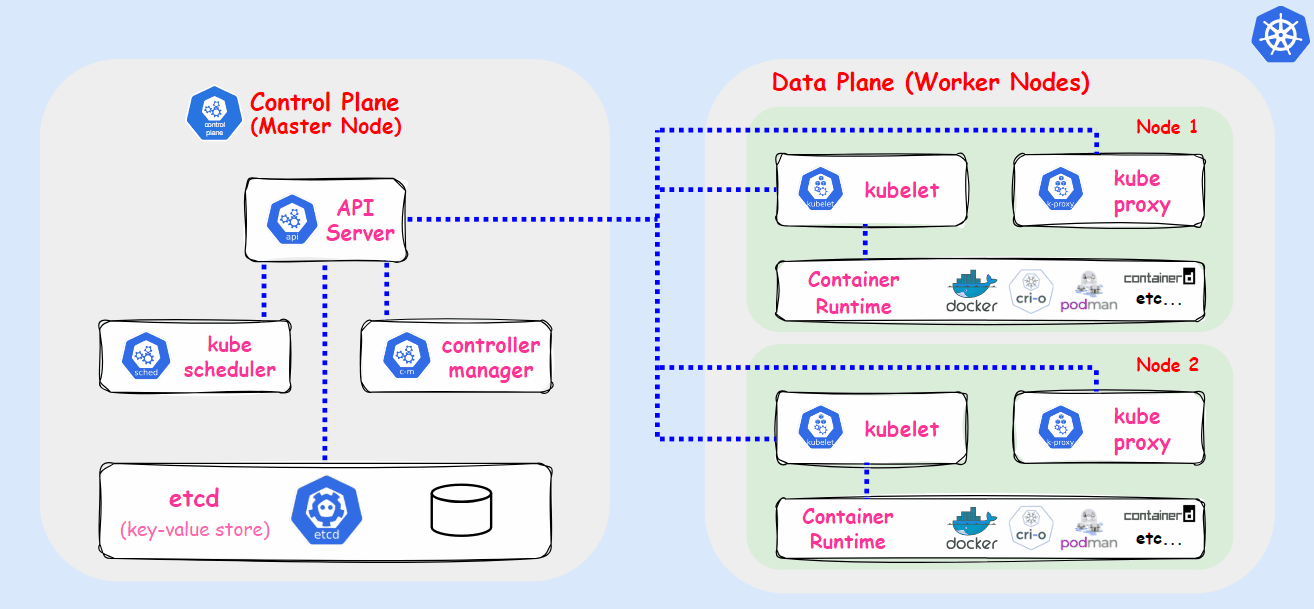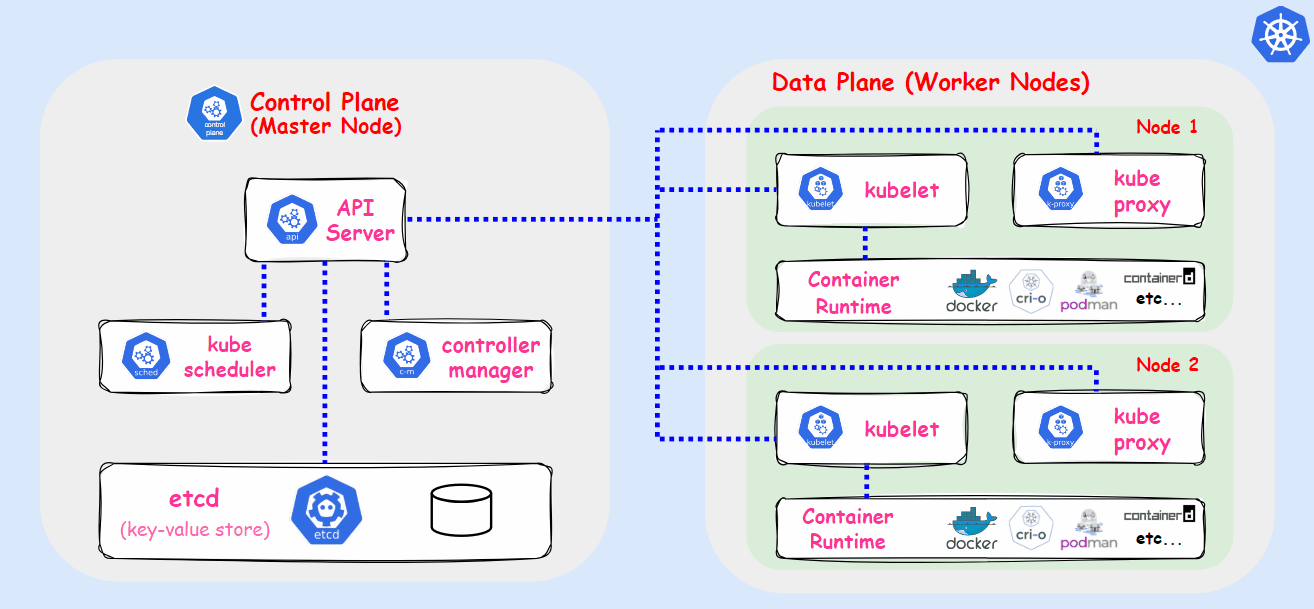
Kubernetes, also known as k8s, is an open-source container orchestration platform developed by Google Lab in 2014. It automates the deployment, scaling, and management of applications housed in containers. Kubernetes allows multiple containers to operate on the same machine and also facilitates the management of container-based applications across multiple machines, which can include various environments such as physical servers, virtual machines, and cloud-native applications.
Kubernetes is not a conventional PaaS system, that is a cloud computing model that provides developers with a platform and environment to build, deploy, and manage applications. It offers key PaaS-like features, including deployment, scaling, and load…